Understanding Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are a group of disorders characterized by the progressive degeneration of the structure and function of the nervous system. These conditions lead to the gradual decline of neurons, which are essential for transmitting signals within the brain and between the brain and body. Among the most prevalent neurodegenerative diseases are Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease, each with distinct symptoms and progression patterns.
Alzheimer’s disease is recognized as the most common form of dementia, significantly impacting memory and cognitive functions. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience disorientation, impaired reasoning, and behavioral changes, leading to increased dependency on caregivers. In contrast, Parkinson’s disease primarily affects movement due to the loss of dopamine-producing neurons, resulting in tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Huntington’s disease, which has a genetic basis, is characterized by uncontrolled movements, cognitive decline, and emotional disturbances. It generally manifests in mid-adulthood, leading to severe impairment over time.
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases, including genetics, environmental influences, lifestyle choices, and overall health. Individuals with a family history of these conditions may have a higher likelihood of developing similar symptoms. Common symptoms across these diseases include memory loss, difficulty concentrating, mood swings, and motor function issues. Understanding the underlying biological mechanisms, which often involve the accumulation of misfolded proteins, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, is crucial in exploring preventive strategies. This foundational knowledge primes exploration into potential interventions such as red light therapy that may offer promising avenues for neurodegenerative disease prevention.
The Science Behind Red Light Therapy
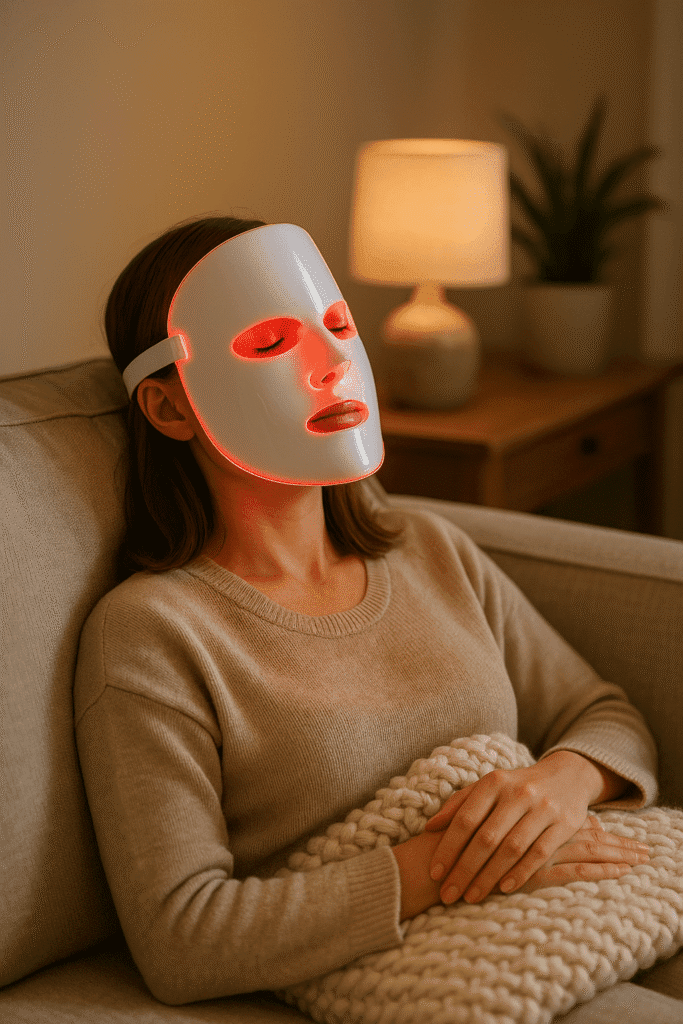

Red light therapy (RLT) operates on the principle of photobiomodulation, a process that involves the absorption of specific wavelengths of light, primarily in the red and near-infrared spectrum, by cellular components. The key players in this cellular interaction are the mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles found in cells.
When stimulated by red light, mitochondria enhance their production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell. This increase in ATP production can bolster cellular functions, thereby promoting cellular repair and rejuvenation. Red light therapy (RLT) operates on the principle of photobiomodulation, a process that involves the absorption of specific wavelengths of light, primarily in the red and near-infrared spectrum, by cellular components.
The key players in this cellular interaction are the mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles found in cells. When stimulated by red light, mitochondria enhance their production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell. This increase in ATP production can bolster cellular functions, thereby promoting cellular repair and rejuvenation.
In the context of neurodegenerative diseases, the efficacy of red light therapy lies in its capacity to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, common underlying factors in diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Studies have shown that RLT can encourage neuroprotection and improve neuronal resilience against damage. By improving mitochondrial efficiency and promoting cellular repair mechanisms, red light therapy has emerged as a promising adjunctive treatment in the prevention and management of neurodegenerative conditions.
Recent clinical studies have provided compelling evidence supporting the application of red light therapy in improving cognitive functions and overall brain health. For instance, randomized controlled trials have demonstrated enhancements in cognitive performance and reductions in symptoms associated with neurodegenerative diseases following regular RLT sessions. The therapeutic effects are attributed to the restoration of mitochondrial functions and the stimulation of neurotrophic factors, which are known to support neuron survival and growth.
Various devices, including laser systems, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and full-body panels, have been developed for red light therapy, each designed to deliver optimal wavelengths to target specific areas of the body. Different protocols exist regarding duration and frequency of exposure, all tailored to meet individual therapeutic needs. As research continues to evolve, red light therapy stands at the forefront of innovative approaches to combatting neurodegenerative diseases.
Red Light Therapy for All Ages: Benefits for Young and Old
Red light therapy has emerged as a promising approach in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases, offering distinct advantages for both younger and older individuals. As individuals age, the brain undergoes cellular changes, often leading to a decline in cognitive function and an increased risk of age-related neurological disorders. Red light therapy, with its ability to stimulate cellular function and promote neuronal health, plays a crucial role in mitigating these effects in older adults. By enhancing mitochondrial activity, red light therapy contributes to improved energy production within brain cells, potentially slowing down the progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Furthermore, studies suggest that red light therapy could enhance neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself, which is particularly beneficial for seniors. This therapeutic approach might help improve cognitive functions such as memory and attention, enabling older adults to maintain their mental acuity longer than they would without such interventions.

On the other hand, the benefits of red light therapy are not limited to the elderly. Younger individuals, especially those with a family history of neurological diseases or those exposed to high-stress environments, can take proactive measures by incorporating red light therapy into their wellness routines. Regular exposure to red light therapy may fortify the brain against the pathological changes associated with neurodegenerative diseases, potentially staving off the onset of symptoms later in life. Additionally, it may enhance mood and sleep quality, leading to improved overall mental health and resilience against stressors.
In essence, red light therapy serves as a versatile tool for individuals across the lifespan, promoting neurological health and better quality of life, regardless of age. This proactive approach could serve as a keystone in both the prevention and management of neurodegenerative conditions.
Complementary Therapies to Maximize Effectiveness
Red light therapy has garnered significant attention as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative diseases due to its capacity to promote cellular health and reduce inflammation. However, the efficacy of this therapy can be enhanced through a comprehensive approach that incorporates various complementary therapies. By integrating lifestyle changes and non-invasive treatments, individuals may better support neurological health and potentially reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions.
One of the key areas to focus on is dietary adjustments. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can provide essential nutrients that help protect neuronal function. Foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, nuts, and berries have been shown to support brain health. Additionally, staying adequately hydrated and limiting processed foods can also lead to better overall health outcomes, further complementing the effects of red light therapy.
Physical exercise is another essential component in promoting brain health. Engaging in regular aerobic exercise, strength training, or flexibility exercises like yoga can have a profound impact on cognitive function and mood stability. Exercise has been proven to decrease inflammation, enhance blood flow, and stimulate the production of neurotrophic factors, all of which can complement the benefits of red light therapy in preventing neurodegenerative diseases.


Mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep-breathing techniques, and tai chi also play a crucial role in enhancing mental well-being. These practices have been linked to stress reduction and improved cognitive performance, and when combined with red light therapy, they may create a comprehensive strategy for maintaining neurological health.
Furthermore, individuals might consider integrating other non-invasive therapies, such as acupuncture or massage. These therapies can alleviate stress and enhance relaxation, offering additional support to the nervous system. When combined with red light therapy, they can contribute to a holistic approach to supporting brain function.